Since 2000
Gottfried, P., Yagil, E. and M. Kolot. (2000) Core-binding specificity of bacteriophage integrases. Molec. Gen. Genet. 263:619-624.
Gottfried, P., M. Kolot, and E. Yagil. (2001) The effect of mutations in the Xis binding sites on site-specific recombination in coliphage HK022. Molec. Gen. Genet. 266:584-590
Aguena, M., E. Yagil, and B. Spira. (2002) Transcriptional analysis of the pst operon of Escherichia coli . Molec. Gen. Genomics 268:518-524.
Kolot, M. and E. Yagil (2003) Determinants that target the integrase of phage HK022 into the mammalian nucleus. J. Molec. Biol. 325:629-635.
Rutkai, E., Dorgai, L., Sirot, R., Yagil, E. and R. Weisberg (2003) Characterization of secondary attachment sites used by phage 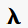 , and a role for such sites in changing phage insertion specificity. J. Molec. Biol. 329:983-996.
, and a role for such sites in changing phage insertion specificity. J. Molec. Biol. 329:983-996.
Kolot, M., Meroz, A. and E. Yagil (2003) Site-specific recombination in human cells catalyzed by the wild type integrase protein of coliphage HK022. Biotechnology and Bioengineering84:56-60.
Gottfried, P., Silberstein, N., Yagil, E and Kolot, M. (2003) Activity of coliphage HK022 excisionase (Xis) in the absence of DNA binding. FEBS Letters 545:133-138.
Taschner, N. P., Yagil, E. and Spria, B. (2004) A differential effect of sS on the expression of the PHO regulon genes of Escherichia coli. Microbiology, 150: 2985-2992.
Gottfried, P., Kolot, M., Silberstein, N. and Yagil E. (2004) Protein-protein interaction between monomers of coliphage HK022 excisionase. FEBS Letters, 577:17-20.
Gottfried, P., Lotan, O., Kolot, M., Maslenin, L., Bendov, R., Gorovits, R., Yesodi, V., Yagil, E. and Rosner, A. (2005) Site-specific recombination in Arabidopsis plants promoted by the integrase protein of coliphage HK022. Plant Molecular Biology 57:435-444.
Pasternak-Tashner, N., Yagil, E., and Spria B. (2006) The effect of IHF on σ S selectivity of the phoA and pst promoters of Escherichia coli . Archives of Micrbiology:185:234-237.
Yemini,M., Levi, Y., Yagil, E. And Rsihpon, J. (2007) Specific electrochemical phage sensing for Bacillus subtilis and Mycobacterium smegmatis . Bioelectrochemistry 70:180-184.
Harel-Levi G., Goltsman J., Tuby CN., Yagil E. and Kolot M. (2008) Human genomic site-specific recombination catalyzed by coliphage HK022 integrase. J Biotechnol. 134 : 46-54.
Kolot M., Gorovits R., Silberstein N., Fichtman B. and Yagil E. (2008) Phosphorylation of the integrase protein of coliphage HK022. Virology. Virology 375:383-390.
Malchin N., Molotsky T., Yagil E., Kotlyar A B. and Kolot M. (2008) Molecular analysis of a recombinase-mediated cassette exchange reactions in Escherichia coli catalyzed by integrase of coliphage HK022. Res. Microbiol. 159:663-670.
Malchin N., Goltsman J., Gorovits R., Bao Q., Dröge P., Yagil, E. and Kolot M. (2009) Optimization of coliphage HK022 integrase activity in human cell. Gene 437:9-13.
Melnikov, O., Zaritsky, A., Zarka, A., Boussiba, S., Yagil, E., Kolot, M. (2009) Site-specific recombination in cyanobacterium Anabaen PCC7120 catalyzed by the integrase of bacteriophage HK022. J. Bacteriol. 191:4458-4464.
Malchin, N., Molotsky, T., Borovok, I., Voziyanov, Y., Kotlyar A.B., Yagil, E. and Kolot, M. (2010) High Efficiency of a Sequential Recombinase-Mediated Cassette Exchange Reaction in E. coli. J. Molec. Microbiol. and Biotechnol. 19:117-122.
Malchin, N., Tuby, C.N., Yagil, E. and Kolot M. (2011) Arm site independence of coliphage HK022 integrase activity in human cells Molec. Genet. and Genomics 285:403-413.
Voziyanova, E., Malchin, N., Anderson, R.P., Yagil, E., Kolot, M. and Voziyanov, Y. (2013) An efficient Flp-Int dual RMCE reaction in mammalian cells. Nucl. Acid Res. e125. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt341. Epub 2013 Apr 29.
Kolot, M., Malchin, N., Elias, A., Gritsenko, N. and Yagil, E. (2015) Site promiscuity of coliphage HK022 integrase as tool for gene therapy. Gene Therapy, In the press.






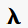 , and a role for such sites in changing phage insertion specificity. J. Molec. Biol. 329:983-996.
, and a role for such sites in changing phage insertion specificity. J. Molec. Biol. 329:983-996.