


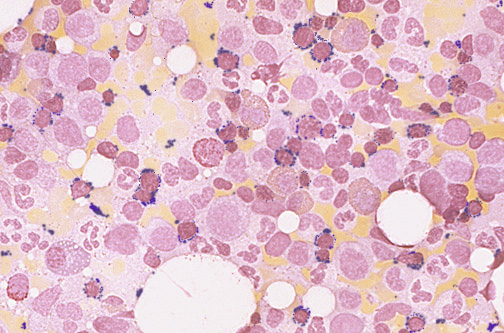
| Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS) are a group of clonal stem cell disorders leading to impaired cell proliferation and differentiation. The precursor erythroid, myeloid, and megakaryocytic cells appear abnormal. The bone marrow may appear normocellular to hypercellular. Morphologic findings include dyserythropoietic changes with nuclear abnormalities, ringed sideroblasts in erythroid precursors, as shown here, hypogranulation and hyposegmentation in myeloid precursors, increased myeloblasts, and reduced numbers of disorganized nuclei in megakaryocytes. There are peripheral blood cytopenias, though most patients initially present with anemia. There is an increased risk for transformation of an MDS to acute myelogenous leukemia. MDS may be primary (idiopathic) or secondary to chemotherapy for cancer. |


 |