


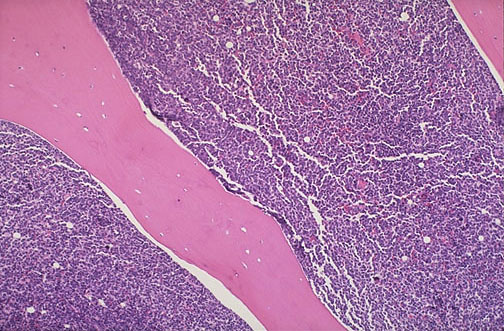
| In contrast to aplastic anemia, leukemia results in a highly cellular marrow. The marrow between the pink bone trabeculae seen here is nearly 100% cellular, and it consists of leukemic cells of acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) that have virtually replaced or suppressed normal hematopoiesis. Thus, though the marrow becomes quite cellular, there can be peripheral cytopenias. This explains the complications of leukemia including infection (lack of normal leukocytes), hemorrhage (lack of platelets), and anemia (lack of red blood cells). |


 |