
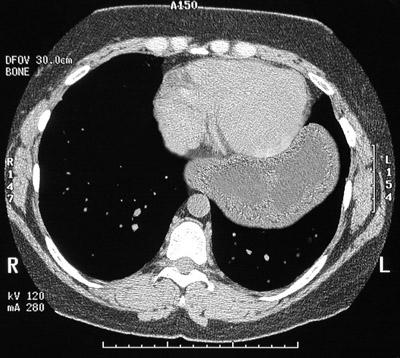
 | This chest CT scan reveals that much of the stomach is seen in the left chest cavity adjacent to the heart. This complication is known as a paraesophageal hernia. The gastric wall is thickened from edema with early infarction from a compromised blood supply with constriction of the arterial supply through the narrow opening to the chest from the upper abdomen through the diaphragm. |


 |