


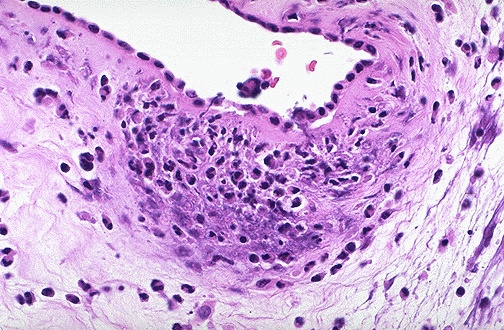
| Premature and/or prolonged rupture of fetal membranes (PROM) increases the risk for intrauterine infection, because bacteria can pass into the normally sealed amniotic cavity. This leads to acute inflammation as seen here as an acute chorioamnionitis within the fetal membranes. The fetus may become infected and suffer intrauterine fetal demise. Also, the inflammation may lead to premature labor and premature birth. |


 |