|
A 23-year-old woman has the sudden onset of dyspnea. She is taken to the emergency department. On examination vital signs show T 37 C, P 100/min, RR 25/min, and BP 100/70 mm Hg. Her lungs are clear to auscultation and no murmurs are heard. An electrocardiogram shows T-wave inversion in leads V1 to V4.
Laboratory findings show Hgb 14.2 g/dL, Hct 42.8%, MCV 91 fL, WBC count 7790/microliter, and platelet count 191,200/microliter. Her D-dimer is 5 (normal <0.5 miccrogram/mL). An arterial blood gas on room air shows pO2 95 mm Hg, pCO2 32 mm Hg, pH 7.46, and HCO3 23 meq/L.
Questions:
3.1 What is your differential diagnosis list?
Pneumothorax
Thromboembolism
Pneumonia
Panic disorder
3.2 What diagnostic studies may be done?
A chest radiograph will help diagnose a pneumothorax. A chest CT scan can be readily obtained and is non-invasive. A pulmonary ventilation-perfusion scan helps diagnose pulmonary embolus, but yields only a "probable" diagnosis. Pumonary angiography is the "gold standard" for diagnosis of thromboembolism, but is invasive and expensive. A D-dimer assay is very sensitive, but lacks specificity, and is best employed as a negative predictor. A sputum gram stain and culture can help diagnose an infection, but she is afebrile.
Example 1:
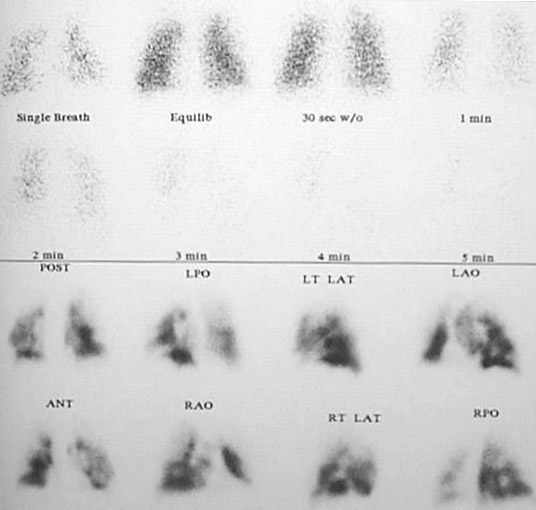
Example 2:
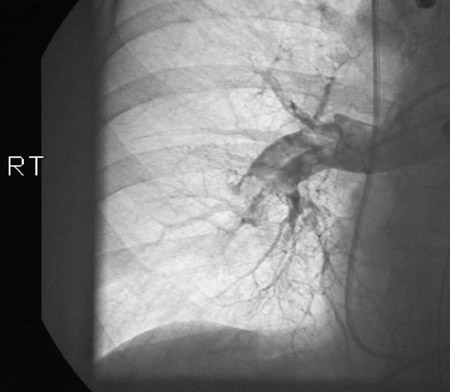
Her V\Q scan shows a high probability for pulmonary thromboembolism. A pulmonary angiogram is ordered and shows thromboemboli in several branches of her pulmonary arterial tree (the charge for the angiogram is subsequently denied by the insurance company).
3.3 What additional studies are indicated?
At her age, an underlying disorder, such as a coagulopathy, should be considered. Subsequent studies show:
| Lupus anticoagulant | negative
| | Prothrombin gene mutation | negative
| | Factor V Leiden mutation | positive
| | Protein C | normal
| | Protein S | normal
| | Antithrombin III | normal
| | Homocysteine | normal
|
3.4 What do these findings suggest?
Factor V Leiden mutation with a hypercoagulable state. Therapy with anti-thrombolytic and anti-coagulant drugs will be discussed further in the hematology organ system.
Drug treatment for panic disorder will be discussed in the CNS section of the course.
| 


