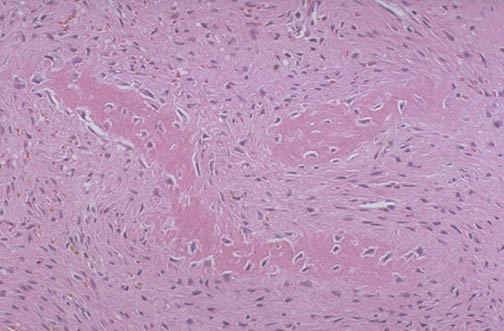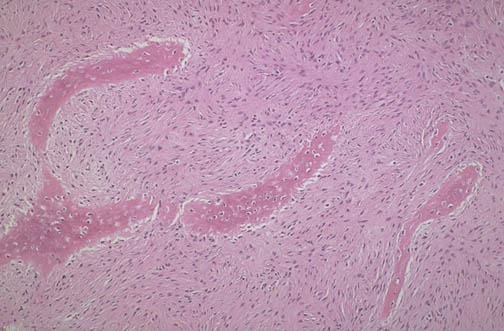
 | Fibrous dysplasia of bone is a non-neoplastic process in which there is a localized area in which irregular woven bone proliferates but does not develop into solid lamellar bone, leaving a weakened area that can produce deformity or fracture. Most cases are monostotic, involving a single area in adolescence. Polyostotic forms often appear earlier in childhood and persist later into adulthood. The McCune-Albright syndrome consists of polyostotic fibrous dysplasia in conjunction with cafe-au-lait spots on the skin and disorders of the endocrine system. In the low power view above and medium power view below, there are irregular spicules of woven bone in a cellular stroma. |


 |