published version |
version of last section |
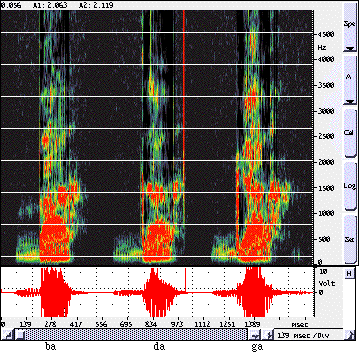
Figure 1 Spectrogram of the syllables /ba/, /da/ and /ga/, uttered by myself.
Figure 3 Hand-painted spectrograms of the syllables ba, da, ga.
The ba--da--ga pitch continuum of F2 is divided into 14 steps instead of three.
The two parallel regions of black indicate regions of energy concentration, F1 and F2.
Notice that the onset frequency of F2 of da is higher than that of ba;
and the onset frequency of F2 of ga is higher than that of da.
I wish to illustrate these two modes of listening through two series of sound stimuli from an unpublished demo tape by Terry Halwes. Listen to the series in figure 2, and see whether you hear the change from [ba] to [da], from [da] to [ga] occur suddenly.
| ba, da, ga |
Let us isolate the second formant transition, that piece of sound which differs across the series, and listen to just those sounds alone.
| Glides and whistles |
A bass singer need not be thick. Look at the picture of Samuel Ramsey, who sings Pimen's part in Mussorgsky's opera Boris Godunov, one of the most illustrious bass parts in the opera literature.

Listen to the first few bars of Pimen's soliloquy sung by Samuel Ramsey, against the following setting:
Night. A cell in the Chudov monastery. Father Pimen is writing by the light of an oil lamp. Grigory is asleep.
Berliner Philharmoniker, Claudio Abbado. Sony:S3K 58 977
Click here
Listen to Peter Ladefoged producing an utterance in which there are no words, but in which the speaker sounds contented