


|
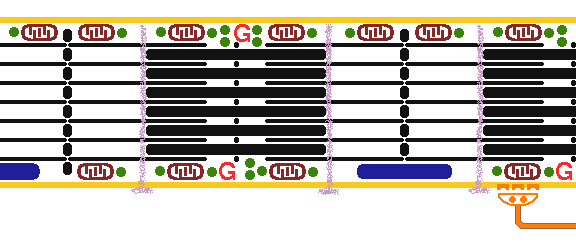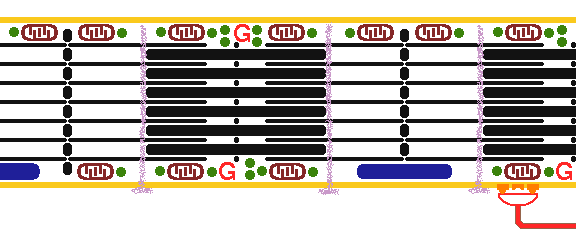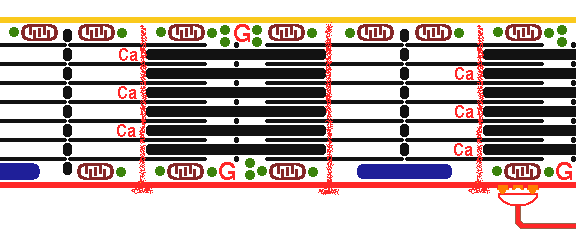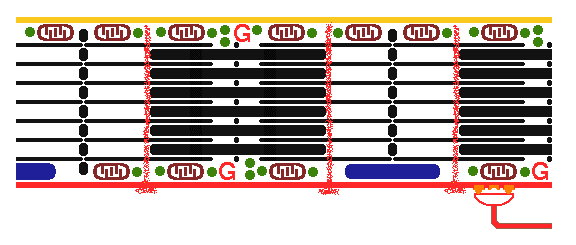
This is normal skeletal muscle contraction. A myelinated nerve impulse conducted to the myoneural junction causes release of acetylcholine, which binds with acetylcholine receptor that leads to depolarization which extends down the T tubules with release of calcium ions. Contraction occurs when actin and myosin filaments slide past each other. The actin filaments have attached tropomyosin molecules which bind troponin, components of which bind actin and bind calcium, which triggers contraction. |


 |