


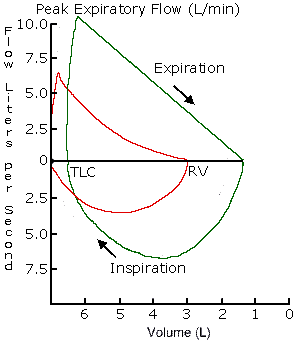
| Above is a flow-volume loop diagrammatic representation of pulmonary function with obstructive lung disease in red, compared to normal in green. |
| Pulmonary Function Testing | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Predicted Value | Observed Value |
| FVC (L) | 5 | 4 |
| FEV1 (L) | 4 | 2 |
| FEV1/FVC (%) | 80 | 50 |
| MVV (L/min) | 100 | 30 |
| TLC (L) | 6 | 7 |
| DLCO (mL/min/mm Hg) | 8 | 20 |
| Note above that the forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) is reduced because of loss of elasticity in distal airways. The TLC is increased because of increased residual volume with air trapping. The DLCO is reduced in advanced obstructive lung disease because of the loss of alveolar walls and dilation of distal airspaces. |


 |