|
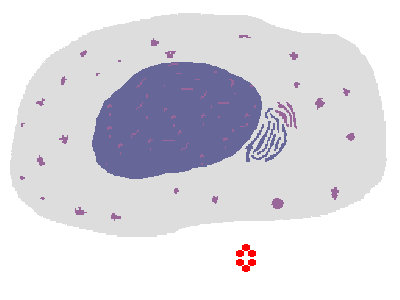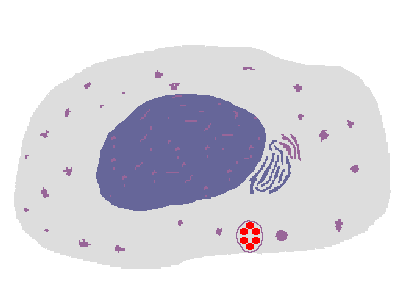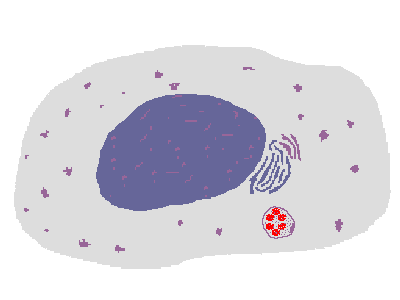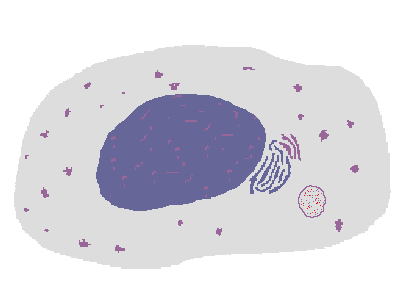
The process of phagocytosis of an infectious agent by a macrophage is shown above. The ingested microbe is contained within a phagosome that fuses with a lysosome in the cytoplasm, yielding a phagolysosome in which the microbe is digested by the lysosomal enzymes. One such enzyme, phagocyte oxidase, converts oxygen to superoxide and creates free radicals (reactive oxygen intermediates). Another enzyme is nitric oxide synthase, which generates nitric oxide that is also toxic to microbes. |