


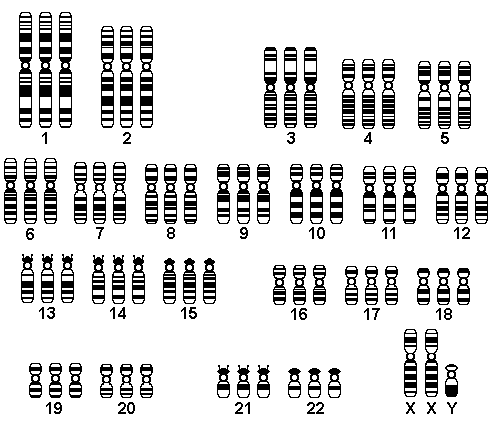
| Triploidy occurs most often when there is double fertilization of an ovum (dispermy), but fertilization of the ovum by a diploid sperm, or failure of loss of the polar body of the ovum may also lead to this event. The resulting karyotype may be 69, XXX or 69, XXY or 69, XYY. The extra set of paternal chromosomes predisposes to formation of a placental partial mole, features of which are often not grossly or microscopically apparent. |


 |