


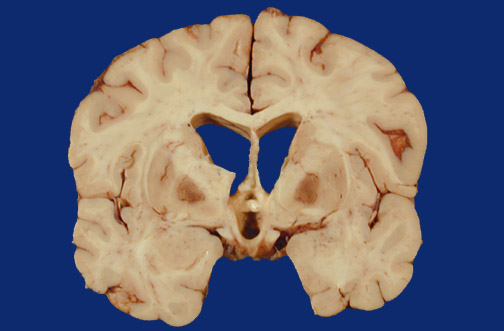
| The globus pallidus bilaterally exhibits evidence for toxic injury with a red discoloration from hyperemia, edema, and necrosis as a consequence of carbon monoxide poisoning. The poisoning may be chronic, with neurologic symptoms appearing somewhat acutely. |


 |